How Medication Management Works in Long-Term Care Facilities
March 18, 2025
Exploring Effective Medication Management in Long-Term Care Settings


Understanding the Importance of Medication Management
Long-term care facilities play a critical role in providing healthcare to older adults, who often have complex medication regimens due to chronic conditions. Proper medication management is vital in these settings to ensure safety, promote adherence, and improve health outcomes. In this article, we explore how medication management works within long-term care facilities, covering the processes, roles of healthcare professionals, technological advancements, and regulatory aspects. By understanding these components, we can appreciate the intricacies involved in managing medications safely and effectively for residents.
The Framework of Medication Management

How does medication management work?
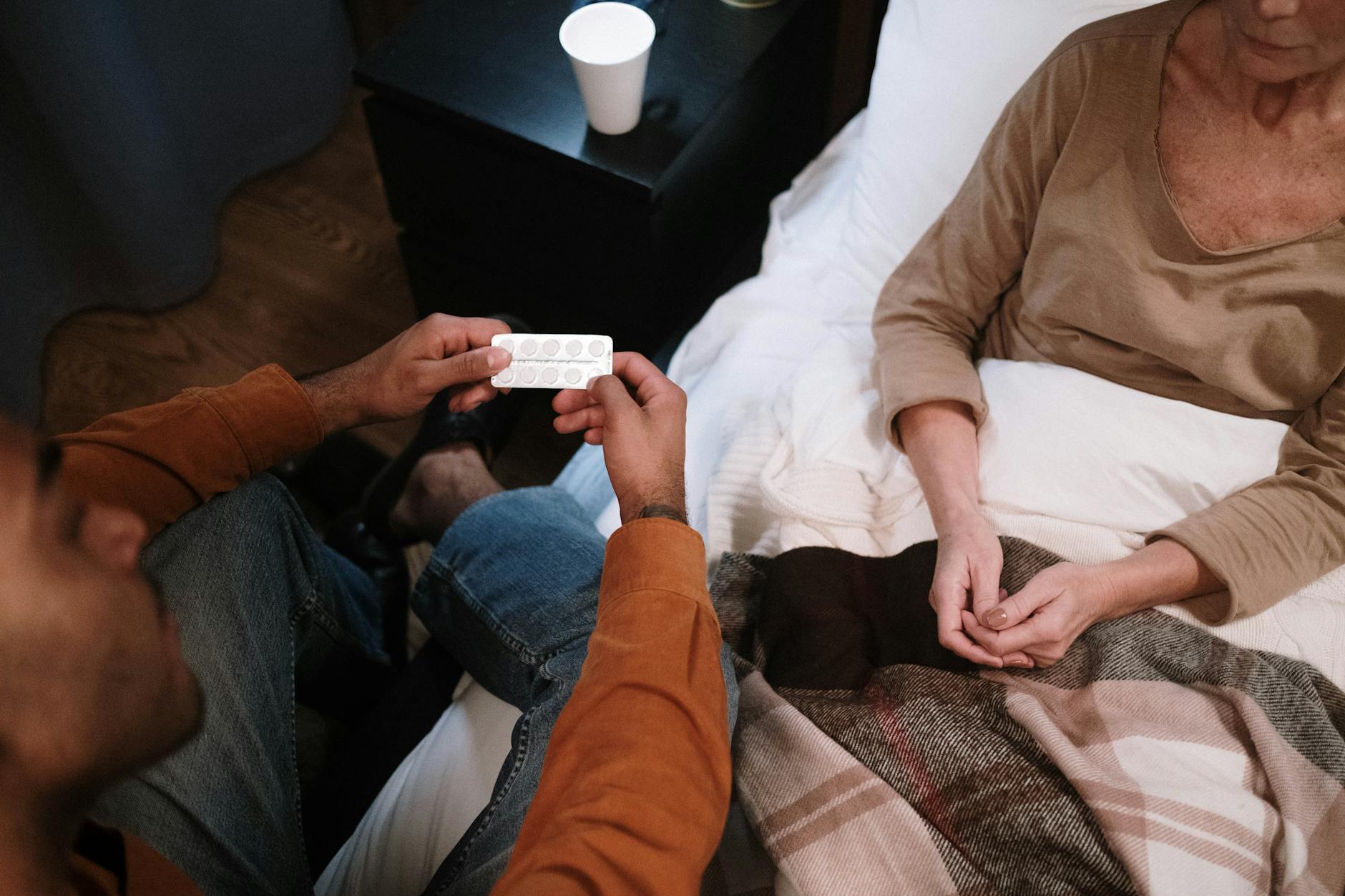
Medication management is a comprehensive process that ensures patients take their prescribed medications safely and effectively to achieve therapeutic outcomes. It encompasses several phases: prescribing, transcribing, dispensing, administering, and monitoring medications. Each stage is vital and must be approached with diligence, especially since errors can occur at any point.
The process starts with a detailed review of a patient’s medications, including a focus on possible drug interactions and side effects. This oversight is essential in all healthcare settings but is especially critical for older adults, who often deal with multiple chronic conditions and complex medication regimens.
Patients receiving medication management are educated about their prescriptions, understanding potential interactions and the spectrum of side effects, which can range from mild issues to serious complications requiring hospitalization. This continuous communication between healthcare providers and patients is foundational, ensuring that therapies are customized according to individual needs while promoting adherence.
What is the significance of effective medication oversight?
Effective medication oversight is essential in fostering safety and improving health outcomes, especially in long-term care environments. Older adults are particularly vulnerable, with estimates showing that between 16-27% experience medication errors. Implementing robust medication management programs can significantly minimize these incidents, ensuring correct documentation and adherence while also addressing systemic issues such as high workload and staff shortages.
Strategies like medication therapy reviews (MTR) and reconciling medications during transitions of care are vital components that drive quality in medication management.
Incorporating technology such as electronic health records (EHR) and automated systems can further streamline processes, notably improving accuracy in prescribing and reducing overall medication errors. As part of a comprehensive healthcare strategy, effective management ensures better therapeutic outcomes and enhances patient safety.
Understanding the Stages of Medication Management

What are the stages of medication management?
Medication management consists of five critical stages that streamline the process to ensure safety and efficacy in patient care. These stages include:
- Ordering/Prescribing: This initial step involves healthcare providers deciding which medications are appropriate for the patient. Accurate information is necessary to prevent issues like look-alike and sound-alike medications.
- Transcribing and Verifying: Once a prescription is written, it must be accurately transcribed into the system. Verification here is vital to avoid errors from miscommunication or illegible handwriting.
- Dispensing and Delivering: This phase focuses on preparing and supplying the medications to the healthcare setting. It is essential to ensure the correct medications are delivered to the right facilities or patients on time.
- Administering: During drug administration, adherence to the proper protocols is crucial. Adverse events often occur at this stage due to various factors like excessive workloads and high-alert medications. The application of the ‘Ten Rights of Medication Pass’ significantly helps in preventing errors.
- Monitoring and Reporting: This final stage involves tracking the patient’s responses to the medication, which can identify any discrepancies or adverse events early. Continuous feedback and education in this phase are essential for refining practices further.
Strategies to minimize errors across these stages include implementing advanced technology, enhancing interprofessional communication, and conducting regular staff education. By focusing on these approaches, healthcare providers can vastly improve medication safety and adherence, particularly for vulnerable populations like older adults.
Guidelines for Safe Medication Administration

What are the guidelines for medication administration in long-term care?
The guidelines for medication administration in long-term care facilities are designed to ensure the safety and effectiveness of medication use. Compliance with federal regulations is essential and encompasses several important aspects:
- Ordering and Recording: Medications must be appropriately ordered and recorded, with checks in place to prevent errors.
- Storage: Medications need to be stored securely, following specific guidelines to maintain their efficacy.
- Administration and Monitoring: Staff must adhere strictly to protocols for administering and monitoring medications to swiftly address any adverse reactions.
- Error Rates: Facilities are mandated to ensure that the medication error rate remains below five percent.
- Monthly Drug Reviews: Regular reviews of residents' drug regimens are crucial for monitoring adverse reactions.
What are the Ten Rights of Medication Administration?
To further minimize medication errors, nursing staff must adhere to the 'Ten Rights of Medication Administration':
| Right | Description |
|---|---|
| Right Patient | Confirm the identity of the patient receiving the medication. |
| Right Medication | Verify the medication being administered is correct. |
| Right Dose | Ensure the correct dosage is given based on the physician's order. |
| Right Route | Administer the medication via the approved route (oral, injection, etc.). |
| Right Time | Follow the prescribed timing for medication administration. |
| Right Documentation | Accurately document the administration of the medication immediately after giving it. |
| Right to Refuse | Respect the resident's right to refuse medication and document the refusal. |
| Right Assessment | Assess the patient's condition before administering medications. |
| Right Evaluation | Monitor the patient for therapeutic and adverse effects post-administration. |
| Proper Hand Hygiene | Perform hand hygiene before and after the administration process to prevent infections. |
These guidelines and rights help maintain a high standard of care and reduce the risk of complications related to medication errors, which can have severe consequences.
Exploring the Rights of Medication Administration

What are the rights of medication administration?
In medication management, the rights of medication administration are foundational to patient safety. Traditionally, they encompass six critical points: the right resident, right medication, right dose, right route, right time, and the right to refuse. This framework is designed to significantly reduce the potential for medication errors within healthcare settings.
As care practices evolve, some facilities expand these six rights into ten, adding aspects such as patient education, assessment, evaluation, and proper documentation. These additions underscore the importance of a holistic approach in medication management that respects the individuality of each resident, ensuring tailored support based on their specific health needs.
Importance of adherence to these rights
Strict adherence to the rights of medication administration enhances the safety and effectiveness of medication management. It not only minimizes the risk of errors but also empowers patients, providing them with the information and respect necessary for making informed choices regarding their care.
Additionally, robust protocols for communication among healthcare professionals, family members, and staff significantly contribute to promoting the individual’s autonomy. Regularly reviewing medication orders and maintaining accurate records are vital to adapting to changes in health conditions, which reinforces safety and therapeutic efficacy throughout the patient’s journey.
Roles and Responsibilities in Medication Administration

Involvement of Healthcare Professionals and Residents
Medication administration in long-term care (LTC) settings involves a variety of healthcare professionals as well as residents themselves.
Healthcare Professionals:
- Registered Nurses (RNs) and Licensed Practical Nurses (LPNs): Are typically responsible for overseeing medication administration, ensuring adherence to the prescribed regimen while monitoring for adverse reactions and effectiveness.
- Certified Medical Technicians: In some instances, they may assist in delivering medications under the supervision of licensed staff.
- Clinical Pharmacists: Conduct reviews of medications, focusing on dosage accuracy and potential interactions to enhance resident safety.
Residents: In many assisted living environments, residents may self-manage their medications if they are deemed capable. Facility policies dictate the extent of this autonomy, which can vary significantly.
Differentiation of Roles Based on Regulations
The roles in medication administration are heavily influenced by state regulations and facility-specific policies.
- Licensed Personnel: Must adhere to established guidelines while administering medications, which include the verified checklist of the 'Ten Rights of Medication Pass.'
- Medication Aides or Technicians: Trained non-licensed personnel can administer medications in certain states, provided they do so under a nurse's supervision.
- Self-Management by Residents: Some assisted living setups promote self-administration, emphasizing the need for residents to understand their medication protocols, but always under the framework of community regulations.
This structure ensures that medication administration within LTC settings prioritizes safety and compliance with healthcare standards.
Navigating Medication Policies in Assisted Living
What are the policies and procedures for medication in assisted living?
Assisted living communities create specific medication management policies that ensure safe and effective medication use. These policies can vary significantly by state and facility, making it essential for families to inquire about the policies relevant to their chosen community.
Typically, staff members in these communities do not perform medication administration directly. Instead, they help facilitate a comprehensive medication management plan that includes tracking medications and focusing on safety to prevent any errors. Some residents may be permitted to self-administer their medications if they demonstrate the ability to do so, under the community's assessment and training guidelines.
The policies often require adherence to critical principles such as the "seven rights" of medication administration, which include verifying the right resident, medication, dose, route, time, documentation, and response. This framework is vital for minimizing errors during administration.
Documentation of any assistance provided during medication management is essential. It ensures compliance with established health regulations and protects both residents and staff by creating a clear record of medication practices and resident actions.
Importance of documentation and regulation adherence
Documentation plays a pivotal role in medication management within assisted living settings. Well-maintained records help track medication usage and adherence, ensuring that any changes in residents' health are appropriately documented and addressed.
Moreover, strict compliance with regulatory guidelines and community policies fosters a safe environment. Staff must be trained to follow the correct processes diligently, from documenting medication passes to respecting residents' right to refuse medications. This adherence not only safeguards resident health but also aligns with state and federal regulations that protect vulnerable populations within assisted living facilities.
Addressing Challenges in Medication Management
Common challenges such as medication errors and polypharmacy
Medication management for older adults, particularly in long-term care facilities (LTCFs), presents several challenges. Medication errors are widespread, impacting 16 to 27% of residents, often due to complexities such as polypharmacy, where individuals may take multiple medications simultaneously. This situation increases the risk of adverse drug events, including incorrect dosages and harmful interactions.
Particularly during transitions of care, the chances of error escalate, where discrepancies in medication lists can lead to serious complications. Older adults may also struggle with memory, vision impairments, and dexterity issues, complicating their ability to self-administer medications safely.
Strategies for medication error prevention
To combat these challenges, various strategies can be implemented. Medication reconciliation is critical during transitions to ensure all medications are accurately documented, reducing the risk of errors. Additionally, education programs promoting medication self-management help residents understand their regimens.
Utilizing technology, like electronic health records (EHR) and automated dispensing systems, can also enhance accuracy in prescribing and administration, effectively mitigating medication errors. Establishing clear communication among healthcare staff, ensuring adherence to safety protocols, and training on the 'Ten Rights of Medication Pass' are further essential steps in fostering a safer medication management environment.
Integrating Technology in Medication Management
Role of technology in error reduction and adherence
In the realm of medication management, technology plays a pivotal role in reducing errors and enhancing adherence, particularly in long-term care settings. The integration of electronic health records (EHR) and computerized physician order entry (CPOE) systems streamlines prescribing and dispensing processes. These systems improve accuracy by minimizing miscommunication and ensuring that healthcare providers have complete and updated medication information at their fingertips.
Moreover, advanced solutions like spencer® are revolutionizing how medications are managed in nursing homes. This automated device not only helps in verifying correct dosages but also issues alerts for any discrepancies. Its ability to provide reminders further supports medication adherence among residents, addressing a critical issue in senior care.
Examples of technological solutions like EHR and spencer®
The following technologies illustrate the advancement of medication management in long-term care:
| Technology | Function | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Electronic Health Records (EHR) | Centralizes patient medication information | Reduces prescribing errors and enhances communication |
| Computerized Physician Order Entry (CPOE) | Streamlines order entry process | Minimizes transcription errors and facilitates rapid access |
| Spencer® | Automated medication management device | Improves accuracy, timely reminders, and reduces errors |
The adoption of these technological tools not only boosts the efficiency of healthcare providers but significantly improves safety and health outcomes for residents in long-term care facilities.
The Impact of Automated Dispensing Systems
Benefits of Automated Dispensing Systems
Automated dispensing systems, such as Spencer®, enhance medication management in long-term care facilities by streamlining the medication administration process. By utilizing pre-filled cartridges, these systems minimize the time spent on medication retrieval and distribution. According to findings, implementing such systems has led to a 71% reduction in medication retrieval time over a 90-day period, significantly improving the availability of medications at critical times.
Additionally, these systems ensure accurate dose verification and provide real-time alerts, which are vital in preventing medication errors. They promote adherence to safety protocols by supporting nurses in meeting the 'Ten Rights of Medication Pass'. With automated reminders for residents, these systems boost medication adherence, resulting in improved health outcomes for older adults.
Cost Savings and Efficiency Improvements
The switch to automated dispensing has substantial financial benefits. Long-term care facilities have reported a 96% reduction in unscheduled medication delivery costs, leading to savings of approximately $8,900. Increased efficiency in pharmacy operations is also evident, with a remarkable decline in labor hours needed for preparing and checking medications—59% and 80%, respectively.
Enhanced inventory management lowers standing medication costs by over $10,000 while increasing urgent medication availability. Overall, automated dispensing systems not only optimize care delivery but also yield significant operational and financial efficiencies.
Regulatory Framework for Medication Management
State and Federal Regulations Impact on Medication Management
Medication management in long-term care facilities (LTCFs) is shaped by a complex web of state and federal regulations. These rules govern every stage of the medication management process, ensuring that residents receive safe and effective care. States often implement their own specific guidelines which are designed to complement federal standards, thus providing a layer of safety for residents with unique needs.
Oversight by Organizations like CMS
The Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) play a pivotal role in regulating medication management within LTCFs. CMS sets forth detailed rules that facilities must adhere to regarding medication administration and safety practices. These include maintaining comprehensive medication inventories and conducting regular drug utilization reviews to prevent medication errors throughout the facility. By enforcing these regulations, CMS ensures that the highest standards of medication safety and quality are upheld for vulnerable populations in long-term care settings.
Improving Medication Safety and Adherence
Educational Strategies and Communication Improvement
Educating both staff and residents is crucial for improving medication safety and adherence, especially in long-term care (LTC) settings. Ongoing training programs can enhance nurses' knowledge about medication management protocols, enabling them to adhere consistently to the 'Ten Rights of Medication Pass.' Regular workshops can address medication complexities, allowing caregivers to recognize and prevent medication errors.
Additionally, establishing clear communication channels among healthcare teams facilitates accurate medication information sharing. This can dramatically reduce errors during medication transitions, particularly when patients are moved between different care settings.
Role of LTC Pharmacies in Enhancing Safety
Long-term care (LTC) pharmacies play an integral role in improving medication management. They provide specialized services including unit-dose packaging, which simplifies medication administration and helps prevent errors. These pharmacies conduct regular medication utilization reviews and offer direct access to clinical pharmacists who perform resident chart reviews, enhancing the safety and efficacy of medications prescribed.
By ensuring timely medication deliveries and maintaining proper inventory controls, LTC pharmacies support healthcare facilities in minimizing risks associated with medication errors. Their involvement can lead to better patient outcomes and increased adherence rates among residents, thereby addressing common challenges in medication management.
Conclusion: Building Better Medication Practices
Effective medication management in long-term care facilities involves a careful balance of comprehensive review processes, adherence to regulations, and utilization of technology. Challenges such as medication errors and adherence issues are addressed through strategic education and communication enhancements. As the role of technology grows, facilities that embrace it alongside structured programs demonstrate significant improvements in patient care and resident satisfaction. Continuous evaluation and adaptation of medication management practices are essential to meet the evolving healthcare needs of long-term care residents and improve their overall quality of life.
References
- Medication Management Technologies for Long-Term and Post ...
- Medication Policy and Procedure for Assisted Living | A Place for Mom
- How Smart Medication Management Can Solve Your Nursing ...
- Linking the processes of medication administration to medication ...
- Medication Administration in Long-Term Care Is Complicated
- Preventing Medication Errors in Assisted Living and LTC
- New Study Highlights Benefits of Medication Management ...



































































.jpeg)






































































































































































































.avif)






















































.jpeg)






























































.jpeg)













.jpg)









































.jpeg)






































































.avif)




.avif)












































.avif)