How to Stay Calm and Collected in Medical Emergencies
February 7, 2025
Mastering Composure: Techniques for Medical Emergency Situations


Introduction: The Importance of Staying Calm
In the high-pressure world of medical emergencies, maintaining a calm and collected demeanor is not just beneficial, it is essential. Whether you're a medical professional, emergency responder, bystander, or family member, having the tools to manage stress and communicate effectively can make a critical difference in the outcome of an emergency situation. This guide explores strategies and insights into maintaining composure, providing the foundational skills to deal with emergencies efficiently.
Understanding Stress and Emergency Preparedness

Physiology of Stress Response
Understanding the physiology of stress is vital for healthcare professionals. The sympathetic nervous system (SNS) triggers a fight, flight, or freeze response during emergencies, preparing the body for immediate action. However, this response can sometimes lead to feelings of panic. Therefore, it's essential for medical professionals to manage these physiological reactions and maintain composure.
Reframing Stress as Beneficial
Instead of viewing stress as an obstacle, nurses can reframe their responses to see these physiological changes as beneficial adaptations. By recognizing that these responses can enhance performance during crises, healthcare workers can build resilience. Techniques such as focusing on the immediate goal (like calling 911) help in reducing feelings of overwhelm, allowing for more systematic handling of emergencies.
Importance of Training and Preparation
Education and ongoing training are crucial in emergency preparedness. Regularly updating skills related to emergency protocols fosters confidence and effective responses. Staying calm and collected can significantly improve decision-making, as stress triggers the body's fight or flight response, which can impair clarity. Practicing mindfulness through deep breathing or meditation can also contribute to this calmness.
This combination of understanding stress physiology, adapting perceptions of stress, and continual training enables professionals to handle emergencies more efficiently, ultimately leading to better patient outcomes.
Practical Techniques for Staying Calm

Breathing Exercises and Visualization
In the face of emergencies, using breathing exercises can significantly help manage stress. Taking a few slow, deep breaths can counter rapid breathing and prevent panic attacks. This technique, coupled with visualization—imagining a calming place—can help ground individuals and promote controlled breathing.
Mindfulness and Relaxation
Practicing mindfulness is essential during high-pressure situations. Engaging in focus-oriented activities, such as counting to ten or a brief three-minute meditation, allows for a reset of one's thoughts. It helps to recognize emotions and shift attention from stressors to mindful awareness, reducing feelings of overwhelm. Furthermore, relaxing facial and body muscles can aid in calming physical responses to stress.
Grounding in Emergencies
Grounding techniques, such as stopping activity to take a moment for calm, help maintain focus on the task at hand. Reminding oneself that ‘it's not your emergency’ encourages prioritization of rational thought over emotional reactions. Establishing a clear single goal during a crisis, like calling 911, can effectively combat overwhelming feelings and allow systematic handling of the situation. These techniques provide frameworks for maintaining composure in chaotic environments.
Effective Communication and Team Dynamics

Role of Communication in Emergencies
Effective communication is vital in emergency scenarios. It reduces stress by ensuring all team members understand their roles and responsibilities. Clear instructions help prevent panic and confusion, leading to more effective patient care outcomes. During high-pressure situations, EMTs and nurses employ concise language and active listening to facilitate coordination.
Defining Roles and Teamwork
Teamwork is crucial in managing emergencies efficiently. By clearly defining roles, team members can focus on their strengths, which enhances overall performance. For example, one member can prioritize patient assessment while others handle communication with families or direct bystanders. This division of tasks streamlines operations and fosters a supportive environment.
Post-Emergency Debriefing
After any emergency situation, a debriefing session is essential. It allows team members to reflect on what worked well and identify areas for improvement. This process not only enhances learning but also strengthens team cohesion. By discussing experiences and emotions, nurses and EMTs can process their responses, improving their readiness for future emergencies.
In summary, effective communication coupled with clear role definitions and a robust debriefing process forms a critical dynamic that enhances emergency response capabilities.
How do emergency responders stay calm?
Emergency responders stay calm by utilizing a range of techniques that enhance focus and decision-making under pressure. They practice positive affirmations, such as "I am in control," and engage in deep breathing to reduce anxiety. Pre-planning and rehearsing for emergencies allow them to anticipate challenges and respond effectively, which helps minimize panic during real situations. Effective communication is critical; they ensure clarity and assign roles to avoid misunderstandings. Finally, assessing the scene for hazards and understanding the urgency of the situation enable them to prioritize actions and provide timely assistance.
Coping Mechanisms and Emotional Responses

How to recognize and manage emotional responses in medical emergencies?
Recognizing and managing emotional responses during medical emergencies is vital. High-stress situations can invoke the body's sympathetic nervous system, leading to a fight-or-flight response. This can manifest as panic, anxiety, or physical symptoms like rapid breathing. To counteract these effects, several techniques can be beneficial:
- Deep Breathing: Engaging in slow, deep breaths can ground you and reduce feelings of panic.
- Counting to Ten: This simple act allows your mind to pause and provides a fresh perspective on the situation, helping to regain composure.
- Physical Activity: Taking a brief walk or stretching can help alleviate stress by releasing endorphins, often referred to as natural mood lifters.
- Gratitude Practices: Identifying something positive can shift your mindset away from stress, enhancing emotional resilience.
For those who find that their stress becomes unmanageable, reaching out for help is crucial. Participating in stress-relief classes or seeking professional support can equip individuals with effective coping strategies for future challenges.
Importance of Self-care Post-Emergencies
Self-care following high-stress incidents is critical for nurses and medical practitioners. Engaging in activities that promote mental and physical well-being is essential to recover from the emotional toll of emergencies. Practicing relaxation techniques, such as meditation or light exercise, can facilitate emotional processing and enhance resilience.
Utilizing Professional Help and Support Networks
It's essential to recognize when stress or emotional response exceeds personal coping capacity. Support networks, including professional help like therapists, can provide valuable tools for managing stress and anxiety. Resources such as the Disaster Distress Helpline can be life-changing in times of need. Establishing a support system ensures individuals have access to reassurance and guidance during challenging situations.
Recognizing and Acting in Emergencies

When should you move a victim in an emergency?
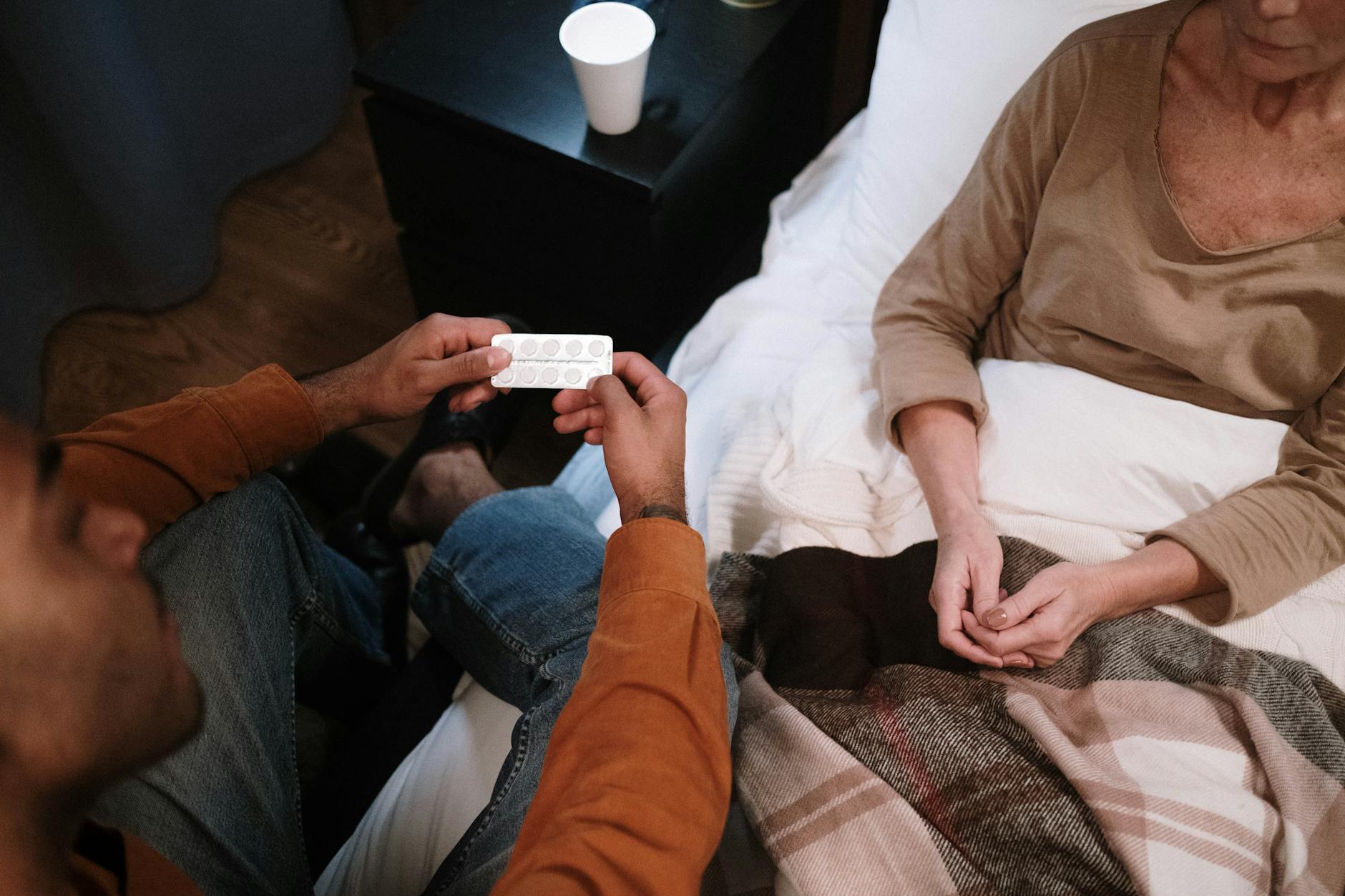
In an emergency, moving a victim should only be considered if it is absolutely necessary. The primary reason for relocation is to prevent further harm or if the victim's safety is compromised due to immediate environmental dangers such as fire, flooding, or traffic hazards. Before making any decision to move, it's crucial to call 911 for professional help.
If the victim is conscious, take a moment to explain your actions and seek their cooperation before proceeding. However, if they exhibit signs of serious injury, such as confusion or severe pain, it is generally advisable to wait for the first responders. If immediate care, like CPR, is necessary, carefully moving the victim may indeed be vital to provide life-saving assistance.
Emergency contacts and information
Organizing emergency contacts and vital health information can significantly enhance response efficiency. Always keep a list of emergency contacts easily accessible, including close family or friends who can provide necessary information about the victim's medical history. This information ensures that responders can provide appropriate care without unnecessary delays.
Additionally, having a medical first aid kit on hand—with essential items like bandages, disinfectants, and any necessary medications—will allow for quick actions to be taken in an emergency.
Essential first aid and CPR knowledge
A solid foundation in first aid and CPR is crucial for effectively handling emergencies. Training in these areas equips individuals with the skills needed to manage a variety of situations, from minor injuries to life-threatening conditions. Being prepared can build confidence and ensure that individuals are ready to act decisively.
Remember, if you witness a medical emergency, don’t hesitate—contact emergency services immediately and provide as much information as possible. Keeping calm while managing the situation can help both the victim and any bystanders maintain composure.
Conclusion: Building Resilience and Readiness
Staying calm in medical emergencies is a skill that can be developed with practice, preparation, and support. By understanding stress responses, applying practical techniques, and fostering effective communication, individuals can enhance their ability to remain composed during crises. Remember, the key to effective emergency management is preparation and practice, ensuring you have the knowledge and tools to handle any situation with clarity and confidence.
References
- Staying Calm During a Crisis: Managing Yourself in an Emergency
- How to Stay Calm in an Emergency | Complete Care
- Stay Calm | Prepare Your Health - CDC
- How To Keep Your Cool In An Emergency? - Idaho Medical Academy
- 5 Ways to Deal with Medical Emergency - First Aid Course Tasmania
- How nurses can keep calm in chaos - The Atlanta Journal-Constitution
- 15 Management Tips for EMTs During High-Pressure Situations
- Keeping Calm Under Stress | Heart and Vascular - Memorial Hermann
- Top 5 Ways to Make a Patient Comfortable During an Emergency
- How to comfort someone in an emergency | British Red Cross



































































.jpeg)







































































































































































































.avif)






















































.jpeg)






























































.jpeg)













.jpg)









































.jpeg)






































































.avif)




.avif)












































.avif)